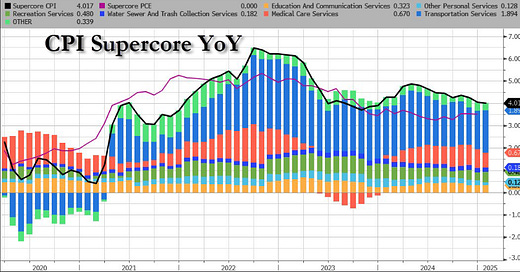
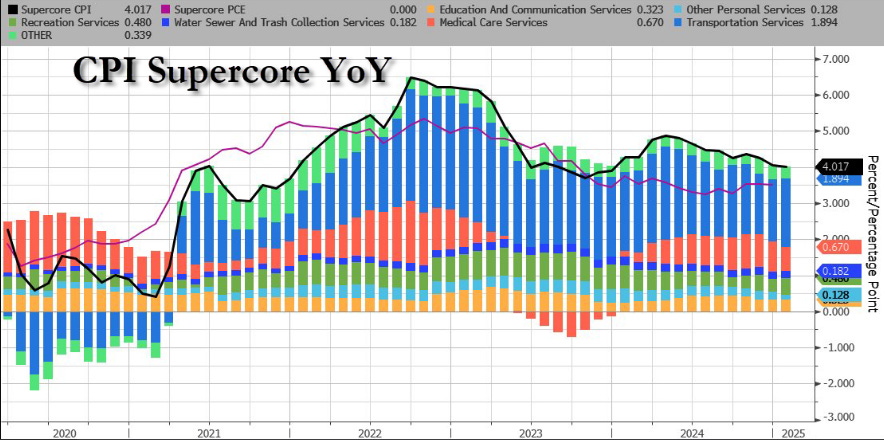
Welcome MTR readers, we warned yesterday of today’s impending inflation data and boy o boy, the FOMC has a pickle on its hands. The headline CPI came in at 0.5% MoM a massive 0.2% higher than the 0.3% expected and YoY a 3.0% rate vs the 2.9% expected. This lead to an increase in Core Consumer Prices to rise at a 3.3% YoY clip. Powell continues his congressional testimony and reiterated that economic activity continues to expand at a “solid pace.” He also stated that “labor is not a source of significant inflationary pressures.” We all know it is the services sector that continues to come in hot. Today’s CPI data saw the FOMCs favorite SuperCore CPI jump 0.7% MoM.
They focus on this SuperCore because it focuses upon “services” inflation and excludes housing. Here we will just provide you with a quick breakdown of the various Consumer Price Index definitions compiled via DeepSeek:
1. CPI (Consumer Price Index)
Definition: The CPI measures the average change in prices over time that consumers pay for a basket of goods and services. It is a key indicator of inflation.
Components: The CPI includes categories like food, energy, housing, apparel, transportation, medical care, and education.
Use: The CPI helps the FOMC assess overall inflation trends in the economy.
2. Core CPI
Definition: Core CPI excludes volatile food and energy prices to provide a clearer picture of underlying inflation trends.
Why It Matters: Food and energy prices can fluctuate significantly due to external factors (e.g., weather, geopolitical events), so Core CPI is often seen as a more stable measure of inflation.
3. SuperCore CPI (FOMCs Focus)
Definition: SuperCore CPI is a more refined measure that focuses on services inflation excluding housing. It typically includes categories like healthcare, education, and transportation services.
Why It Matters: The FOMC pays close attention to SuperCore CPI because services inflation is often more persistent and less sensitive to short-term economic shocks. It provides insight into long-term inflationary pressures.
FOMC's Focus on SuperCore CPI
Persistent Inflation: Services inflation, as captured by SuperCore CPI, tends to be stickier and harder to control than goods inflation. This makes it a critical focus for the FOMC when setting interest rates.
Wage Pressures: Services inflation is closely tied to wage growth, which can drive long-term inflation trends. The FOMC monitors SuperCore CPI to gauge the impact of labor market conditions on inflation.
Policy Decisions: If SuperCore CPI remains elevated, the FOMC may maintain higher interest rates to curb inflation, even if other measures (like Core CPI) show signs of easing.
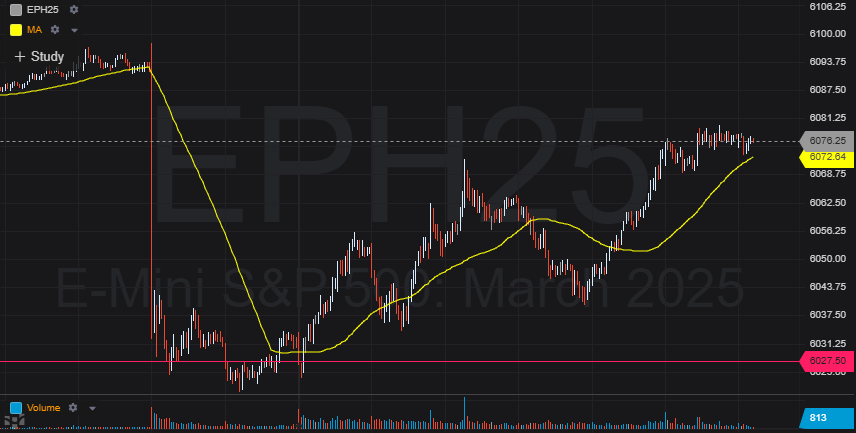
Ok hopefully that helps. As far as the initial markets reaction the equity markets were hit pretty hard and sold off, here is a pic of the SP500 futures move initially dropping 60+ points but buyers willing to close the gap on this as buyers have stepped in all morning long:
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Magnelibra Trading & Research to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.